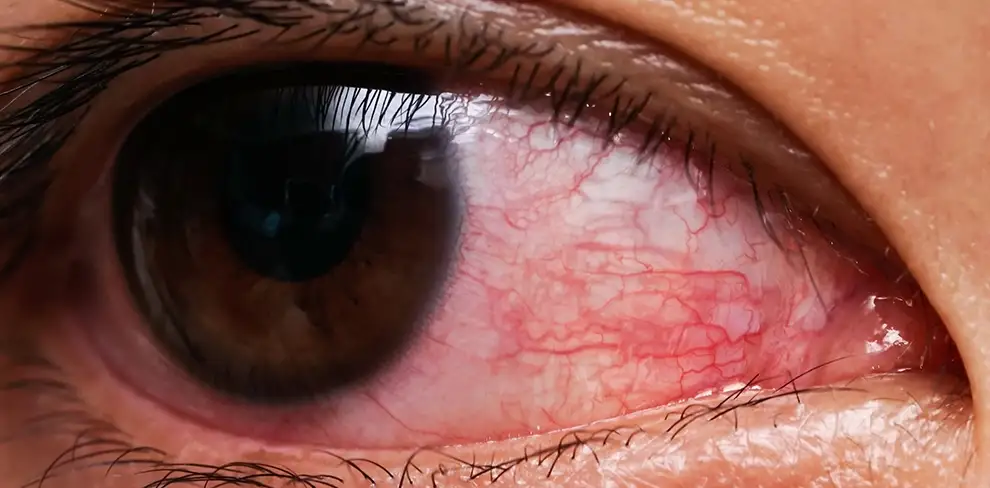
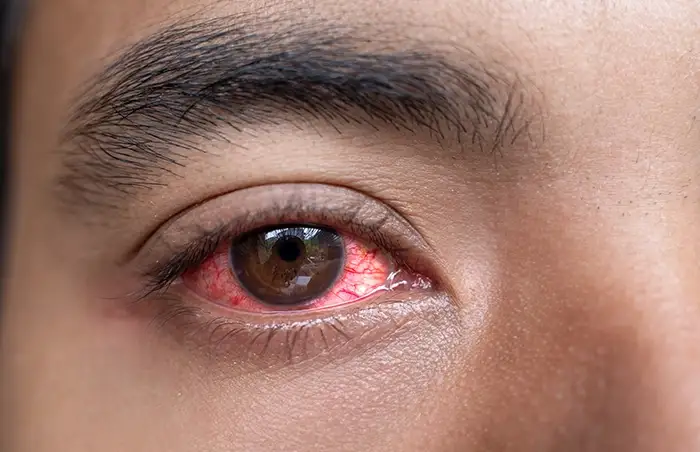
Uveitis is a type of eye inflammation. It hurts the middle layer tissue(uvea) in the eyewall.
The alarming signs often come on suddenly and get severe rapidly. The primary symptoms include eye redness, pain, and blurred vision. The state can affect one or both eyes, and it can affect people of all ages, even children.
Probable reasons for uveitis are infection, injury, or an autoimmune or inflammatory disorder. Several times the doctors can't even identify a cause.
Uveitis can be dangerous, driving to permanent loss of vision. Prior stage diagnosis and treatment are essential to limit complications and protect your eyesight.
Let us discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment before answering the mentioned question.
Causes of Uveitis
The causes of uveitis are often unknown and usually occur in healthy people. It can sometimes be linked with other ailments such as an autoimmune disease or an infection from a virus or bacteria. An autoimmune disease may arise when your immune system hits your body's part. Autoimmune diseases that may be connected with uveitis include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriasis
- Arthritis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Crohn's disease
- Sarcoidosis
Infections are another cause of Uveitis, includes:
- AIDS
- Herpes
- CMV retinitis
- West Nile virus
- Syphilis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
- Histoplasmosis
Other possible causes of uveitis may involve:
- Exposure to a toxin that enters the eye
- Bruising
- Injury
- Trauma
Symptoms of Uveitis
The symptoms and characteristics of Uveitis may involve:
- Eye redness
- Eye pain
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Dark, floating spots in your area of vision (floaters)
- Decreased vision
Treatment of Uveitis
If an underlying condition causes uveitis, treatment may focus on that specific condition. Usually, the treatment for uveitis is the same regardless of the associated reason, as long as it is not infectious. The treatment intends to minimize the inflammation in the eye and other parts of the body if present. In some cases, the patient may need treatment for months to years. Various treatment options are available.
- Drugs that reduce inflammation- The doctor may first prescribe eyedrops with anti-inflammatory medicine, such as a corticosteroid. Eyedrops are generally not sufficient to treat inflammation beyond the front of the eye, so the doctor may prescribe an anti-inflammatory injection in or around the eye or anti-inflammatory tablets.
- Drugs that fight bacteria or viruses- If an infection causes uveitis, your doctor may recommend antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other medicines, with or without anti-inflammatory drugs, to bring the condition under control.
- Vitrectomy- The operation to eliminate some of the vitreous in your eye is sometimes used to diagnose or control the condition.
- A medication-releasing implant- For people with difficult-to-treat posterior uveitis, a device implanted in the eye may be an option. This device gradually releases corticosteroids into the eye consecutively for two to three years.
Complications
If you ignore the symptoms of uveitis and it is left untreated, it can cause complications, including:
- Retinal swelling
- Retina scarring
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts
- Optic nerve damage
- Retinal detachment
- Permanent vision loss
No ophthalmologist can guarantee you the cure of uveitis, but you can get relief from the pain and swelling if treated on time. You can consult the best ophthalmologists at Renuka Eye Institute and get international standard uveitis treatment in Kolkata.